Torn between choosing Amazon FBA vs Dropshipping for your business model? This guide will help you decide which one is the best fit for your goals.
When starting a business on Amazon, selecting the right business model is a crucial step. Your choice will impact your operations, costs, and long-term success.
By deciding early, you can focus on the right strategies to grow your business on Amazon. This helps streamline your budget, inventory, and fulfillment process.
In this guide, we’ll discuss two popular business models: Amazon FBA and Dropshipping. You’ll learn their differences, benefits, and drawbacks to make an informed decision.
Table of Contents
Understanding Amazon FBA
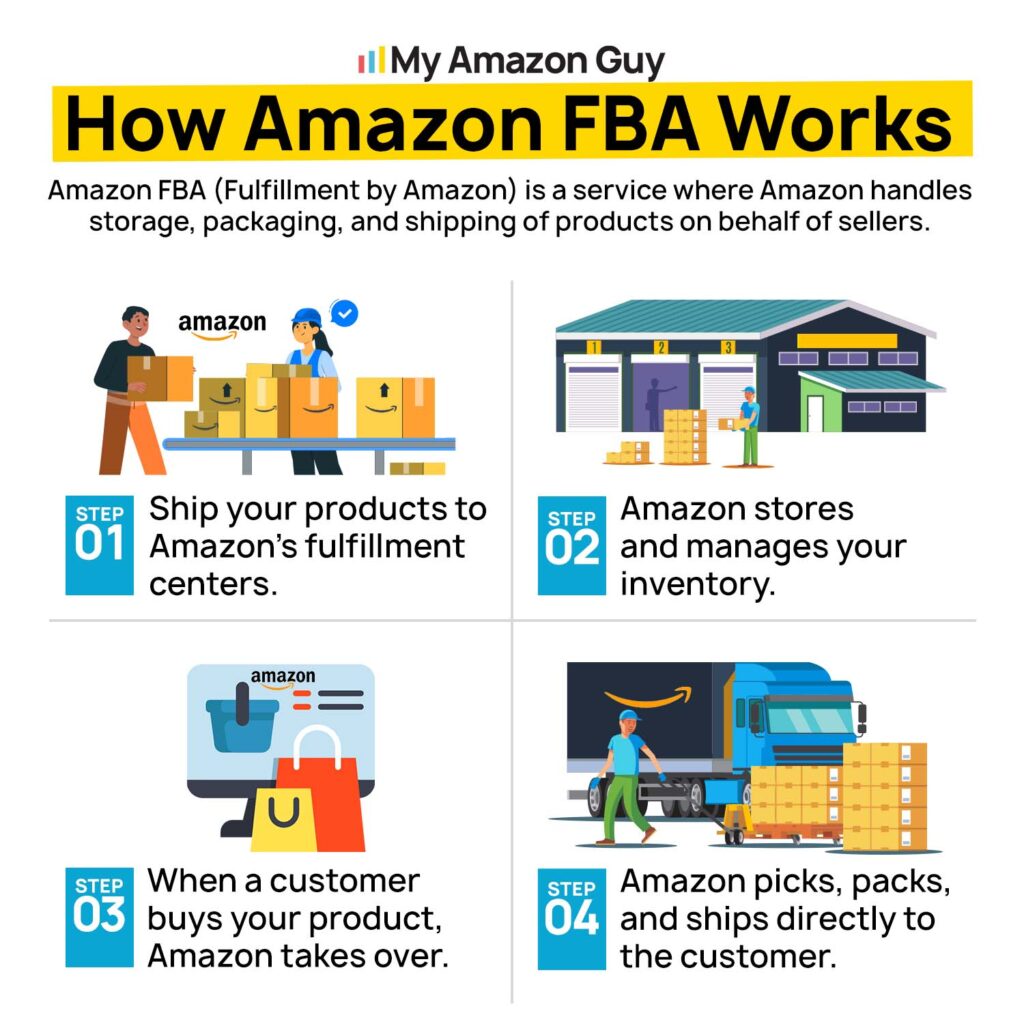
Amazon FBA (Fulfillment by Amazon) is a service where Amazon handles storage, packaging, and shipping for sellers. Most Amazon sellers use FBA because it simplifies logistics and allows them to scale faster.
Sellers send their products to Amazon’s fulfillment centers, where they are stored until sold. When an order is placed, Amazon picks, packs, and ships the product while also managing customer service and returns.
Pros and Cons of Using Amazon FBA
Amazon FBA provides many benefits, making it an attractive option for sellers looking to simplify fulfillment. By outsourcing storage and shipping to Amazon, sellers can focus on business growth instead of logistics.
However, like any business model, FBA has its challenges that sellers must consider. Understanding both the advantages and drawbacks will help you answer the question: Is Amazon FBA worth it?
Pros of Amazon FBA
- Selling through FBA aligns your business with Amazon’s trusted reputation, increasing buyer confidence.
- FBA products qualify for Amazon Prime, making them eligible for fast, free shipping, which can boost conversion rates.
- FBA sellers have a better shot at winning the Buy Box, which leads to more visibility and sales.
- Amazon takes care of storage, packaging, shipping, and returns, allowing sellers to focus on growing their business.
- With Amazon handling fulfillment, sellers can expand without worrying about warehouse space or logistics.
Cons of Amazon FBA
- Amazon charges for storage, fulfillment, and additional services, which can cut into profit margins, especially for low-cost products.
- Amazon manages returns and customer inquiries, which can lead to generic responses and less control over issue resolution.
- If inventory sits too long in the warehouses, sellers face high Amazon FBA storage fees, making slow-moving products a financial burden.
- Amazon requires specific product preparation before sending inventory to fulfillment centers, adding extra time and costs.
- Storing inventory in multiple Amazon warehouses means sellers must comply with different state tax regulations, complicating tax management.
If you want to learn more about Amazon FBA and how it works, enroll in the best Amazon FBA course from MAG School.
Understanding Dropshipping on Amazon
Dropshipping on Amazon is a business model where sellers list products without holding inventory. Instead of stocking goods, sellers rely on third-party suppliers to fulfill orders directly.
When a customer makes a purchase, the seller forwards the order details to a supplier, who then ships the product. This allows sellers to operate with minimal upfront investment while using Amazon’s large customer base.
Pros and Cons of Using Dropshipping on Amazon
Dropshipping on Amazon offers a unique way to sell products without managing inventory or handling fulfillment. This makes it an attractive option for sellers looking for a low-risk entry into e-commerce.
Similar to Amazon FBA, dropshipping has its own set of challenges that can impact profitability. Understanding the advantages and drawbacks will help you determine if it’s the right fit for your business.
Pros of Amazon Dropshipping
- Sellers don’t need a large upfront investment since they only pay for products after making a sale, reducing financial risk.
- There’s no need to handle inventory, packaging, or shipping, making it easy to start selling with a reliable supplier.
- Dropshipping allows sellers to offer a wide variety of products without purchasing stock in bulk, making it easier to test different markets and trending items.
- Since inventory and fulfillment are managed by third-party suppliers, sellers can operate their business from anywhere.
- Suppliers handle storage and shipping, freeing up time for sellers to focus on marketing, product research, and customer acquisition.
Cons of Amazon Dropshipping
- Buying individual units instead of bulk inventory leads to higher product costs and lower profit margins.
- Dropshipping is highly competitive, with many sellers offering the same products, making it harder to stand out.
- Sellers rely on suppliers for product accuracy and quality, increasing the risk of negative reviews due to incorrect or defective items.
- Unlike FBA, where Amazon manages customer service, dropshipping sellers must handle inquiries, complaints, and returns themselves.
- Shipping times can be slow, especially if products come from overseas, which can result in customer dissatisfaction.
Key Differences Between Amazon FBA vs Dropshipping
Understanding the key differences between Amazon FBA and dropshipping helps sellers make informed decisions. By comparing these models, sellers can determine which one best fits their business structure and operational preferences.
Here are the main differences between the two:
1. Business Operations & Seller Responsibilities
Amazon FBA
Sellers purchase inventory in bulk and send it to Amazon’s fulfillment centers. Amazon handles storage, packing, shipping, and customer service, while sellers focus on sourcing, branding, and marketing.
Dropshipping
Sellers don’t hold inventory. Instead, they list products and forward orders to third-party suppliers, who handle fulfillment. Sellers are responsible for marketing, order management, and maintaining supplier relationships.
2. Inventory Management
Amazon FBA
Sellers must invest in inventory upfront and monitor stock levels to avoid overstocking or running out. While Amazon stores and ships the products, Amazon FBA storage fees apply, especially for slow-moving items.
Dropshipping
No upfront inventory is required. Sellers purchase products only after making a sale, eliminating storage costs. However, if a supplier runs out of stock, sellers may face order fulfillment issues.
3. Brand Control
Amazon FBA
Amazon controls most of the buying experience, including packaging and customer service. Sellers have limited branding opportunities but benefit from Amazon’s reputation and trust.
Dropshipping
Sellers can customize branding, packaging, and messaging, offering more control over their business identity. However, unreliable suppliers or shipping delays can negatively impact brand reputation.
4. Customer Base
Amazon FBA
Sellers tap into Amazon’s massive customer base, benefiting from built-in traffic and shopper trust. Organic sales are easier to generate, especially for Prime-eligible products.
Dropshipping
Sellers must actively drive traffic through advertising, SEO, and social media marketing. Building customer trust takes time, and acquisition costs can be high.
5. Order Fulfillment
Amazon FBA
Amazon handles storage, packaging, and shipping, ensuring fast Prime delivery. Once inventory is sent to Amazon, fulfillment is fully automated.
Dropshipping
Suppliers ship orders directly to customers. Shipping times vary depending on supplier location, which can lead to delays and potential customer dissatisfaction.
6. Customer Trust & Reputation
Amazon FBA
FBA products qualify for Prime, which boosts customer trust with fast shipping and easy returns. This can lead to higher conversions and more consistent sales.
Dropshipping
Without Prime eligibility, sellers must build trust from scratch. Long shipping times and potential quality issues can lead to negative feedback and disputes.
7. Costs & Expenses
Amazon FBA
Requires upfront investment in bulk inventory and incurs Amazon FBA storage fees. While costs add up, faster shipping and increased sales potential can offset expenses.
Dropshipping
Startup costs are lower since sellers only pay for products after a sale. However, marketing expenses for customer acquisition can be significant.
8. Profit Margins
Amazon FBA
Higher profit margins due to bulk purchasing at lower costs. However, Amazon’s fees for storage and fulfillment reduce overall profitability.
Dropshipping
Lower margins because per-unit costs are higher when buying from suppliers individually. High competition can make it challenging to maintain profitable pricing.
Dropshipping vs Amazon FBA: Which One Is Right for You?
Now that you understand the differences between Amazon FBA and dropshipping, the next step is deciding which model aligns with your business goals. If you’re still unsure, take this quick quiz to help determine which one is right for you.
FAQs About Dropshipping vs Amazon FBA
What does Amazon FBA mean?
Amazon FBA is a service where sellers store their products in Amazon’s warehouses. When a customer places an order, Amazon takes care of packing, shipping, and customer support, making it easier for sellers to manage their business.
Is Amazon FBA the same as dropshipping?
No, Amazon FBA and dropshipping are different business models. With Amazon FBA, sellers purchase inventory upfront and send it to Amazon’s fulfillment centers. In dropshipping, sellers do not hold inventory.
Does Amazon handle everything for Amazon FBA?
Amazon manages fulfillment, including storing inventory, packing, shipping, and handling customer service for FBA orders. However, sellers are still responsible for product sourcing, inventory management, and marketing.
Which can make you more money: Amazon FBA vs dropshipping?
Amazon FBA generally has higher profit margins because sellers buy products in bulk at lower costs. While dropshipping has lower startup costs, profit margins tend to be thinner due to higher per-unit costs and intense competition. However, profitability depends on your business strategy, niche, and ability to scale.
Is Amazon FBA better than dropshipping?
It depends on your goals and resources. Amazon FBA is better if you want higher sales potential, Prime eligibility, and a hands-off fulfillment process. However, dropshipping is better if you prefer a low-cost, low-risk business model with more control over branding and product selection.
Comparing Amazon FBA vs Dropshipping
The right choice between Amazon FBA and dropshipping depends on your business goals, budget, and how much control you want over operations.
- Amazon FBA is best if you want a hands-off fulfillment process, Prime eligibility, and higher profit margins.
- Dropshipping is ideal if you have limited startup capital and prefer flexibility with branding and product selection.
Each model has its advantages and challenges, so the key is choosing the one that aligns with your long-term business strategy.
Looking for an Amazon FBA agency that could help with your business? Consult our full-service Amazon agency to develop a winning strategy for your business!